Effect of platelet-rich plasma on muscle injuries associated with physical exercise
Alessandro Novaes Prestes, Luiz Alfredo Braun Pereira, Ivo Ilvan Kerppers, Wagner Menna Pereira, Claudia Santos Oliveira, Mario Cesar da Silva Pereira, Afonso Shiguemi Inoue Salgado
Med Sci Tech 2012; 53(2): RA81-86
ID: 883579
Available online:
Published: 2012-11-19
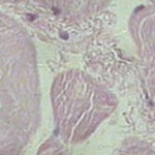
Background: Muscle structure is affected by daily trauma, particularly during sports activities, and is constantly affected by the inflammatory process. Contusions and strains are the most common injuries.
Material/Methods: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), derived from processing autologous blood in a laboratory, is considered rich in growth factors (GF) and has been used to accelerate the regenerative process. The aim of the present study was to assess the correlation between physical exercise and PRP in muscle regeneration.
Results: A greater activation of macrophages, as well as increased degeneration, was found in Group 3 (G3) in comparison to G2. There was a greater vascular and fibrillar organization in G4 than in G3, as well as hypertrophy and hyperplasia of myocytes.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated that the use of PRP is efficient in accelerating the process of muscle regeneration when used in an isolated manner, and its effect is potentiated when integrated with therapeutic exercise.
Keywords: platelet rich plasma, Aerobic exercise, muscle injury treatment, physiotherapy in sports



