Effect of Water Pillar Shower Bathing On Sleep Onset Latency
Hiroyoshi Matsushita, Masaaki Tanaka, Masayuki Kondo, Fumie Komatsu, Ikuto Ueyama, Yasunari Nakajima, Shinji Tanaka, Minoru Sato, Akira Ishii, Yasuyoshi Watanabe
Med Sci Tech 2016; 57:88-94
DOI: 10.12659/MST.900800
Available online: 2016-09-07
Published: 2016-09-07
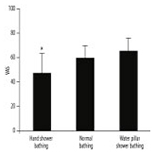
BACKGROUND:
Sleep plays an important role in health promotion, and increased skin temperature is thought to promote rapid sleep onset. The objective of this study was to investigate whether the use of a shower bathing device with a water pillar design would increase skin temperature during the bathing and sleep periods and have a sleep-inducing effect.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
In this crossover experiment, 10 healthy male volunteers were randomized into three groups of different types of shower bathing: normal bathing, normal shower bathing, and water pillar shower bathing. After a 10-minute bathing period, a 20-minute period during which they dried off and put on sleep wear, and a 40-minute rest period, participants moved to a bed and lay in a supine position with their eyes closed for 60 minutes.
RESULTS:
The participants in the water pillar shower bathing group reported being able to fall asleep more easily than the normal shower bathing group. Sleep onset latency was shorter in the water pillar shower bathing group than in the other two groups. Skin temperatures were higher in the water pillar shower bathing group than in the normal shower bathing group throughout the bathing and sleep periods, but no significant differences were seen in rectal temperatures between these two groups during most of the sleep period.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that water pillar shower bathing increases skin temperature and thereby promotes more rapid sleep onset.
Keywords: Baths, Body Temperature, Hydrotherapy, Sleep Stages



