Effects of Pollen Typhae Flavonoids on Atherosclerosis in ApoE–/– Mice
Ruo-lan Huang, Xiao-zhu Liu, Yin-feng Li, Ling Wang, Lai-qing Li, Xiao Chang, Li-jun Ou, Ming-tai Chen, Zhong Zhang
Med Sci Tech 2017; 58:1-9
DOI: 10.12659/MST.903286
Available online: 2017-02-10
Published: 2017-02-10
BACKGROUND:
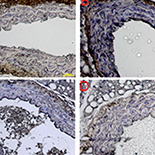
Atherosclerosis is a systemic disease with focal rupture of vulnerable plaque and is responsible for major clinical events. Vascular smooth muscle cells play key roles in the progression of atherosclerosis. Pollen Typhae flavone is a traditional Chinese herb and had been used to treat many diseases. However, effects of pollen Typhae flavonoids on atherosclerosis are unclear. In this study, ApoE–/– mice were fed with high-fat chow to build an atherosclerosis model.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
Different doses of pollen Typhae flavone treatments were used to investigate the effects of pollen Typhae flavonoids on atherosclerosis.
RESULTS:
Results showed that medium-dose and high-dose pollen Typhae flavonoids reduced atherosclerosis lesion area in ApoE–/– mice. Pollen Typhae flavonoids also significantly altered plasma lipid levels, including total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL, and homocysteine. Furthermore, medium-dose and high-dose pollen Typhae flavonoid relieved endoplasmic reticulum stress and lessened inflammation and apoptosis in vulnerable plaque.
CONCLUSIONS:
Pollen Typhae flavonoids are effective in alleviating atherosclerosis by relieving endoplasmic reticulum stress-initiated apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Keywords: atherosclerosis, Intracranial Arteriosclerosis, Orthodontic Appliances, Functional



